Tech
The 7 Emerging Technologies and Innovations That Will Shape the Tech Industry from 2022 to 2030

1. Blockchain
By now, everyone has heard that blockchain will change virtually every market in existence.
The development of a decentralized digital ledger that tracks and maintains information in numerous places, making fraud difficult, might theoretically assist various sectors, including banking, politics, and healthcare.
Complex mathematical procedures, along with skills and expertise, are used to provide identification, making identity theft extremely unlikely.
But there’s one word that leaps out in that description: Decentralized.
Financial institutions, governmental bodies, and healthcare facilities have vested interests in maintaining unfettered authority (unless on their terms).
Thus, while the blockchain space may see some progress, it will likely remain on the technological periphery and fail to spark the revolution its supporters hoped for.
2. Digital Currencies That Use Cryptography
Cryptocurrencies, which are frequently discussed in the same breath as blockchain, apply these similar ideas to allow online commerce (again in a decentralized fashion, which is one of its main appeals).
Many people think cryptocurrency is the wave of the future regarding money.
That’s a great idea, in theory. However, there are two significant problems with cryptocurrencies:
- Its primary allure (apart from unlawful dealings) is that it is hip and fashionable. It was never supposed to maintain the level of attention it received in 2017, and it certainly won’t recover from the unrelenting foolishness of the crypto-bros. The technology is viable; however, there is currently no large-scale need for it.
- There is never any time when cryptocurrencies aren’t on the verge of a bubble. Combine that with the fact that governments and banks will try to discredit its decentralized nature, and you can rest assured that it will remain the irrelevant plaything that Chad (there’s always a Chad) keeps bringing up at frat parties.
3. Emotion-Based Artificial Intelligence/Computing
In 2020, AI was ubiquitous, but it’s not quite as entertaining as we had hoped.
If you’ve been living under a rock, here’s a summary of artificial intelligence: Access to enormous datasets (e-commerce, social media, etc.) and improvements in computing power have enabled businesses to develop statistical models on steroids that can adapt to new information over time.
Affective AI would then extend this methodology to encompass feelings.
Effectively, a computer program may determine your emotional state from your appearance (by training a deep learning algorithm on face data), your writing, or your speech and recommend an appropriate good or service. In a good mood?
How about a commercial for a frappuccino from Starbucks to extend the party?
Is your mood low right now? How about an ad for frozen coffee from Starbucks to brighten your day?
Do not fret, however, for this technology has a well-deserved reputation for being unreliable.
4. AI Cloud Services, Data-as-a-Service, and AI Platform-as-a-Service
When a new technology first enters the mainstream, it is often viewed as incremental rather than revolutionary.
This may be one of the reasons why people have been so dissatisfied with AI as of late.
Only large corporations have reaped the benefits of automating processes that formerly required human input. In contrast, small businesses and individuals have been left to rely on somewhat antiquated computation methods.
While insufficient funds may be to blame, the real issue here is the available information.
This might not last forever. To feed their data-hungry machines, businesses realize that renting an algorithm is a win-win situation.
AI markets and platforms are increasing, promising to supply algorithms tailored to address individual users’ problems (chatbots and digital assistants are only the beginning).
This trend is expected to increase as more and more programmers participate in the gig economy, and their jobs become automated.
This would help both large corporations and sole proprietors improve their day-to-day operations. If you feel that would be detrimental to the group’s psyche, then don’t do it.
5. Smart Houses/Connected Houses
Artificial intelligence (AI) in the home is already famous and is expected to grow in popularity over the next several years.
In reality, we’re already used to having intelligent home assistants like Google’s Nest and Amazon’s Alexa fine-tuning the parameters of our intelligent devices.
However, the value to customers will grow dramatically as more features are added to these services, as is the case with most internet-related offerings.
A single algorithm that can accomplish three different jobs at once, such as making coffee, opening blinds, and raising the temperature in the bathroom when it senses someone has woken up, is much more valuable than the sum of three different algorithms doing these jobs.
6. 5G
Internet-connected devices can’t afford to be as slow as the first iPhone (shots fired); instead, they need to transfer enormous amounts of data dependably. For this reason, we have 5G.
Using higher-frequency radio waves, 5G is the natural progression from 4G and allows for significantly faster transfer rates.
- Despite appearances, a few key phrases must be grasped to appreciate just how challenging it will be to roll out 5G globally.
- Millimeter waves, or extremely short-wavelength radio waves, are those with frequencies between 24 and 100 GHz. This band of the electromagnetic spectrum is not only underutilized but also has the potential for high-speed data transfer, although at the expense of range.
- Microcells, femtocells, and picocells are miniature cell towers used as relays in congested indoor environments. This infrastructure is essential since, as was said up top, the distance at which 5G data can be transferred is significantly less than that of 4G. (And struggles to go through thick walls).
- Massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) enables the transmission and reception of voluminous data from and to various devices.
- Beam-forming requires careful planning and coordination of all these handoffs. What beam-forming does is achieve this.
- Full Duplex, or simultaneous bidirectional data transmission and reception on the same frequency. The speed and quantity of data communicated and the quality of the connection will all be improved by orders of magnitude thanks to this technology, which will have far-reaching effects across many different sectors. It will enable significant developments in virtual reality and the Internet of Things (IoT), among other things, such as linking autonomous vehicles and drones to the internet. As a result, 5G is not something to be trifled with.
7. Mega-Constellations of Satellites / Low-Earth Orbit Satellite Systems
Regarding the World Wide Web… SpaceX hopes to link the entire planet to the internet by deploying 42,000 satellites over the next four years.
Amazon has also revealed intentions to deploy 3,236 low-orbit satellites to cover white areas, and rival competitor OneWeb expects to launch 600 satellites by 2022.
The low price at which these nano-satellites (which weigh only a few pounds) may be launched makes all this conceivable.
Additionally, if fleets were flying at a lower height, management would be much simpler and less polluting.
However, the deployment of so many objects in space increases the chance of collision, disrupts astronomical observation, and interferes with other satellite services like weather forecasting.

Tech
Boost Your Telegram Channel Promotion with KYG’s Services

Telegram channels are powerful tools for businesses aiming to enhance brand awareness, share valuable content, build active communities, improve customer relationships, and boost sales. However, effective telegram promotion and management requires strategic efforts. This article explores how KYG’s services can support your Telegram channel promotion, leveraging advanced tools and strategies to maximize engagement and growth.

Services for Telegram Channel Promotion
Creating engaging content is critical for any social media platform. On Telegram, diverse content types such as text, media, and polls can captivate your audience. KYG’s services can assist in developing a content strategy that resonates with your target audience. With tools to set clear objectives and KPIs, KYG ensures you monitor key metrics and adjust your strategy based on performance and feedback.
Cross-Promotion Tactics
Expanding your reach through cross-promotion is vital. KYG supports cross-promotion efforts by providing insights into the most effective platforms for your audience. Whether you’re leveraging other social media channels or partnering with similar communities, KYG’s analytics help identify and optimize these opportunities, ensuring you attract engaged and interested users.
Influencer Partnerships
Influencer marketing is indispensable for boosting engagement and communication. KYG’s platform aids in identifying influencers who align with your brand values and target audience. By facilitating clear collaboration proposals and tracking campaign results, KYG ensures that your influencer partnerships are both effective and measurable, driving more users to your Telegram channel.
Exclusive Offers and Contests
Offering exclusive content and running contests are proven methods to boost engagement. KYG can streamline the process of advertising these offers across various platforms, ensuring maximum visibility. Additionally, KYG’s analytics tools help monitor the effectiveness of these campaigns, providing valuable insights for future strategies.
Consistent Communication and Engagement
Maintaining an active community requires consistent engagement. KYG’s community management tools make it easier to plan and track communication efforts. By providing comprehensive analytics and personalized recommendations, KYG helps ensure that your Telegram channel remains vibrant and engaging. Responding to comments, rewarding active members, and monitoring community health are all simplified with KYG.
Why Choose Know Your Group
KYG offers a comprehensive suite of tools and services designed to support effective Telegram channel promotion. With KYG, you get:
- Advanced Analytics: Monitor engagement, growth, and performance with precision.
- Customizable Community Portals: Tailor your community space to reflect your brand’s identity.
- Streamlined Onboarding: Easily integrate new members into your community.
- Monetization Tools: Turn your engagement into revenue with various monetization strategies.
- Expert Support: Benefit from personalized recommendations and strategic growth insights.
Know Your Group ensures your Telegram channel thrives, driving engagement and achieving your business goals.
FAQs
What is the best way to create engaging content for a Telegram channel?
Utilize diverse content types like text, media, and polls, and tailor your content to your audience’s interests and needs. KYG’s tools can help set clear objectives and track content performance to make necessary adjustments.
How can KYG help maintain consistent communication on Telegram?
KYG’s tools streamline communication planning and tracking, making it easier to engage with your community regularly. Their analytics provide insights to improve engagement strategies continuously.
What makes KYG a good choice for Telegram channel promotion?
KYG offers a comprehensive suite of tools for community management, including content strategy, cross-promotion, influencer partnerships, and engagement tracking, all tailored to help your Telegram channel succeed.
Tech
Coingama Exchange Review

Coingama is emerging as a premier cryptocurrency exchange platform, designed to cater to both beginner and seasoned traders. With its user-friendly interface, advanced security measures, and comprehensive trading tools, Coingama aims to provide a seamless and secure trading experience. This review delves into the various features and benefits that make Coingama a standout choice in the crowded cryptocurrency exchange market.
User Experience: One of the defining features of Coingama is its intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface. The platform is designed with user experience in mind, making it accessible even for those new to cryptocurrency trading. The registration process is streamlined, allowing users to set up their accounts quickly and start trading without unnecessary delays. The dashboard is well-organized, providing users with all the necessary tools and information at their fingertips. Additionally, Coingama offers a mobile application, enabling users to trade on-the-go with the same level of efficiency and security as the desktop version.
Security Measures: Security is a paramount concern for any cryptocurrency exchange, and Coingama excels in this area. The platform employs a range of advanced security measures to protect users’ funds and personal information. These include two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption, and the use of cold storage for the majority of users’ assets, which significantly reduces the risk of hacking. Coingama also conducts regular security audits and updates to ensure that its security protocols remain robust and up-to-date. Users can trade with confidence, knowing that their assets are safeguarded by some of the most advanced security measures in the industry.
Trading Features and Tools: Coingama offers a comprehensive suite of trading features that cater to a wide range of traders. The platform supports numerous trading pairs, including major cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, as well as various altcoins. This wide selection allows traders to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of different market opportunities. Coingama also provides advanced trading tools, including real-time charts, technical indicators, and market analysis, which help users make informed trading decisions. The platform’s trading engine is designed for high performance, ensuring fast and reliable execution of trades even during periods of high market volatility.
Liquidity and Fees: Liquidity is a crucial factor for any exchange, and Coingama ensures ample liquidity across all trading pairs, allowing for smooth and efficient trading. The platform has partnered with several liquidity providers to maintain tight spreads and minimize slippage. When it comes to fees, Coingama is competitive, offering a transparent fee structure with no hidden charges. Trading fees are kept low to attract more users, and there are various incentives and promotions available that further reduce the cost of trading on the platform.
Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential for any trading platform, and https://coingama.com/ excels in this area as well. The exchange offers 24/7 customer support through multiple channels, including live chat, email, and a comprehensive FAQ section. The support team is responsive, knowledgeable, and dedicated to resolving any issues that users may encounter. This level of support ensures that users can trade with confidence, knowing that assistance is readily available whenever needed.
Educational Resources: Understanding the importance of education in trading, Coingama provides a wealth of educational resources for its users. The platform offers tutorials, webinars, and articles that cover various aspects of cryptocurrency trading, from basic concepts to advanced strategies. These resources are designed to help traders enhance their knowledge and improve their trading skills, making Coingama an excellent choice for both learning and trading.
Conclusion: In conclusion, Coingama is a reliable and efficient cryptocurrency exchange that offers a comprehensive trading environment. Its user-friendly interface, robust security measures, advanced trading tools, ample liquidity, competitive fees, and excellent customer support make it an attractive option for traders of all levels. Whether you are just starting out in the world of cryptocurrency trading or are an experienced trader looking for a dependable platform, Coingama provides the features and support needed to succeed. With its commitment to security, innovation, and user satisfaction, Coingama is well-positioned to become a leading player in the cryptocurrency exchange market.
Tech
Exploring the World of possiblyethereal

possiblyethereal is not just another online platform; it’s a digital sanctuary for seekers of wisdom, inspiration, and connection. Let’s delve into what makes possiblyethereal a unique and enriching experience for its visitors.
What is possiblyethereal?
At its core, it is a multifaceted platform that offers a blend of insightful content, community engagement, and personal development resources. It aims to transcend the mundane and explore the realms of the ethereal, sparking curiosity and fostering personal growth.
Content Categories on possiblyethereal
From thought-provoking articles to immersive multimedia experiences, it covers a wide range of topics. Whether it’s philosophy, spirituality, creativity, or wellness, visitors can find content that resonates with their interests and aspirations.
Unique Perspectives and Insights
What sets this apart is its commitment to offering unique perspectives and deep insights. Through diverse voices and unconventional narratives, the platform challenges conventional thinking and encourages exploration of the unknown.
Interaction and Participation Opportunities
Engagement is key at possiblyethereal, with opportunities for readers to interact through comments, forums, and collaborative projects. The platform fosters a sense of community where ideas are shared, discussed, and celebrated.
User-generated Content
A highlight of possiblyethereal is its emphasis on user-generated content. Visitors are encouraged to contribute their own stories, reflections, and experiences, creating a dynamic tapestry of collective wisdom and creativity.
Ethical Considerations and Transparency
In an era of digital information overload, It prioritizes ethical content creation and transparency. Clear policies ensure that content is authentic, respectful, and aligned with the platform’s values.
Personal Growth and Development
Beyond intellectual exploration, It offers resources for personal growth and development. From mindfulness practices to actionable insights, visitors can embark on a journey of self-discovery and empowerment.
Conclusion
It is more than a website; it’s a portal to a world of infinite possibilities and profound discoveries. Whether you seek intellectual stimulation, spiritual insights, or simply a sense of belonging, possiblyethereal invites you to explore, engage, and evolve.
FAQs
Can I contribute my own content to possiblyethereal?
- Yes, It welcomes user-generated content. You can share your stories, insights, and perspectives with the community.
What types of topics does possiblyethereal cover?
- It covers a wide range of topics, including philosophy, spirituality, creativity, wellness, and more.
How can I engage with the possiblyethereal community?
- You can engage by commenting on articles, participating in forums, and joining collaborative projects.
Are there resources for personal development on possiblyethereal?
- Yes, It offers resources such as mindfulness practices, actionable insights, and inspirational content for personal growth.
What are possiblyethereal’s policies on content creation and transparency?
- It maintains ethical standards in content creation and ensures transparency in information dissemination, aligning with its values of authenticity and respect.

 Others10 months ago
Others10 months agoDavid T Bolno: Why Giving Back To The Community Is So Crucial

 Travel10 months ago
Travel10 months agoPractical And Essential Car Interior Accessories To Add Comfort And Convenience To Your Drive

 Travel10 months ago
Travel10 months agoBusiness Visa for CANADA

 Business10 months ago
Business10 months agoTop Reasons Why you Need to Consider Outsourcing Real Estate Photo Editing

 Health10 months ago
Health10 months agoGarlic Is The Best Vegetable To Treat Heart Problems
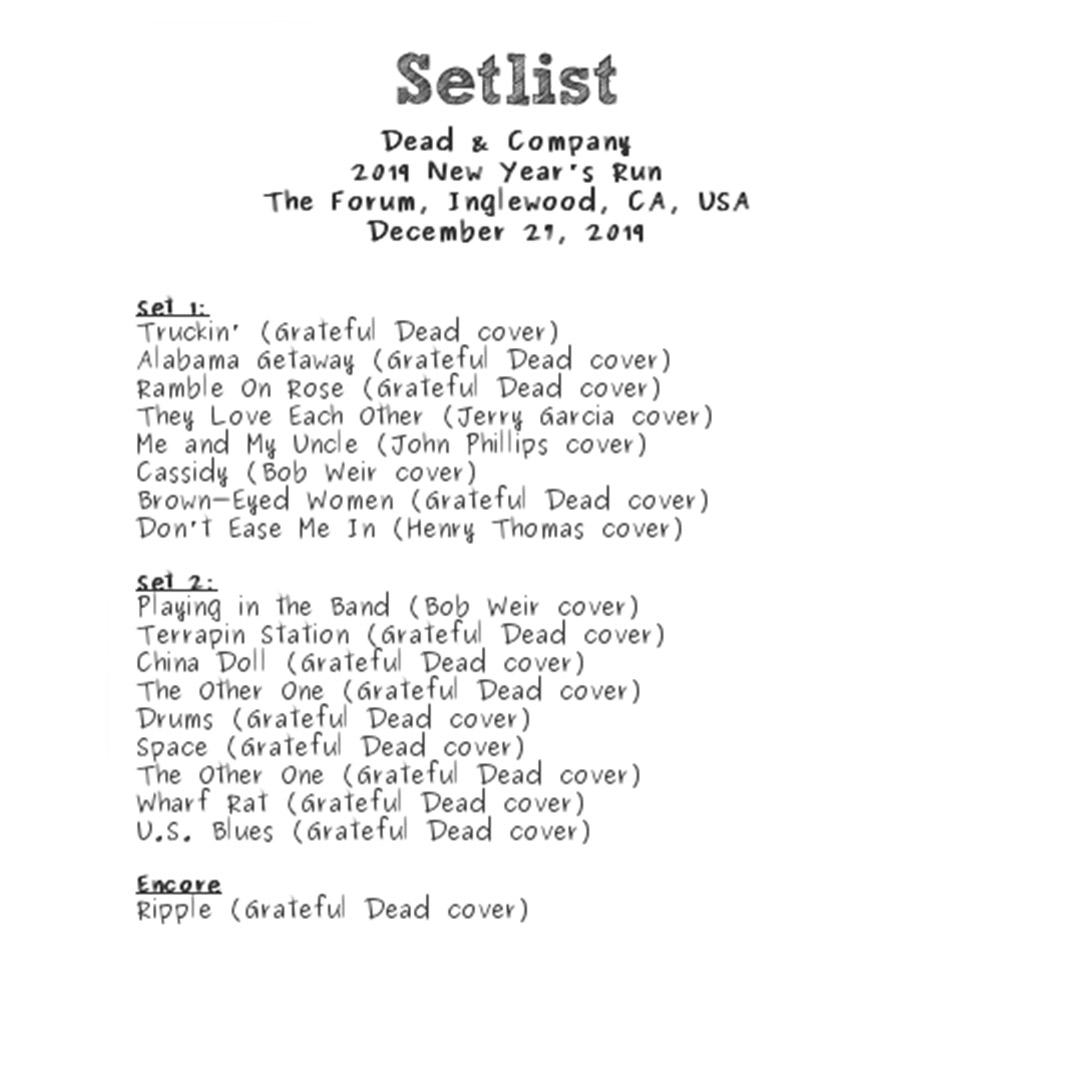
 Business10 months ago
Business10 months agoDead And Co Setlist What They Played At The Gorge Amphitheatre

 Fashion10 months ago
Fashion10 months agoTips For Choosing The Right For Engagement Diamond Rings

 Tech10 months ago
Tech10 months agoThe Best Way to Never Get Lost: Buy Wayfinding Signs!